- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
Why Does the Reading on a Handheld Combustible Gas Detector Keep Jumping Around?
2025-12-03
In industrial testing and safety inspection scenarios, accurate measurement of gas concentration is crucial. When using testing equipment, frequent and unstable fluctuations in values not only make it difficult to determine whether the gas concentration is normal but may also affect safety decisions. These numerical jumps are not random; they are mostly related to the equipment's condition, environmental interference, or operating methods. A step-by-step investigation is needed to find the cause. Zetron Technology's editor analyzes this as follows; let's discuss it together.
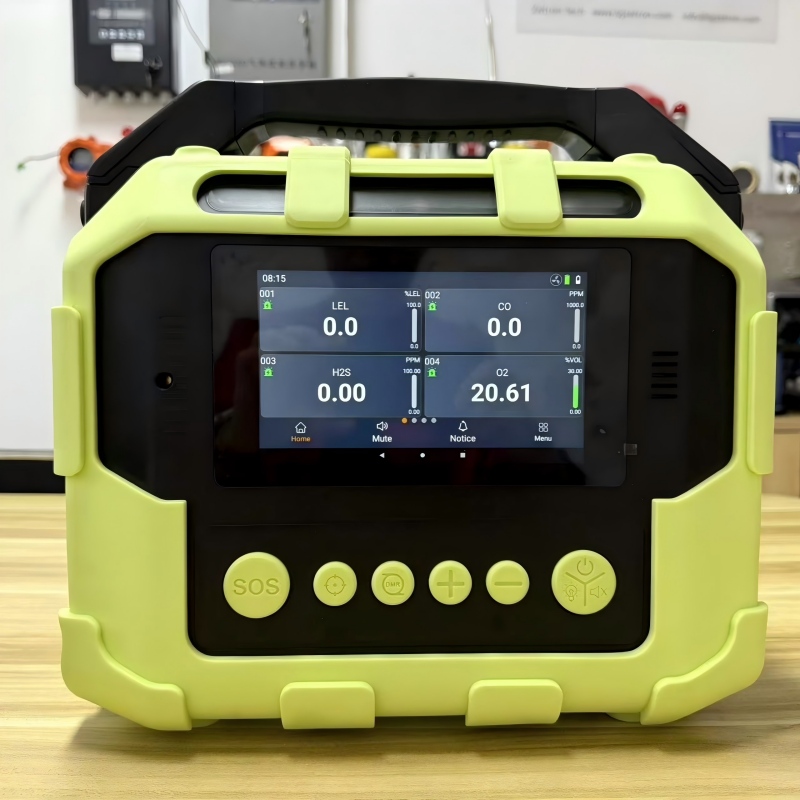

I. Equipment Issues: Sensor or Hardware Failures
The sensor is the core of a combustible gas detector. If the sensor malfunctions or its performance deteriorates, it can easily lead to abrupt changes in readings. For example, as the sensor ages, its internal components deteriorate, reducing its sensitivity to gas and causing unstable readings. Oil, dust, or moisture on the sensor surface can obstruct contact between the gas and the sensing element, causing signal fluctuations and resulting in abrupt changes in readings. Hardware failures can also cause this. Poor contact in the internal circuitry of the combustible gas detector, such as a loose connection between the sampling pump and the main board, or oxidation of the battery interface, can lead to unstable power supply, affecting the transmission and display of detection data. If the sampling pump's performance deteriorates, with fluctuating pumping speeds, the gas flow rate into the sensor will be unstable, causing the readings to fluctuate with the airflow.
II. Environmental Interference: Influence of Airflow or External Substances
Changes in airflow in the detection environment are a common cause. When detecting near vents, fans, or in windy outdoor areas, airflow can disperse or concentrate flammable gases, causing fluctuations in the gas concentration at the sensor and resulting in fluctuating readings. In enclosed spaces, movement of people creating localized airflow can also interfere with gas distribution, leading to abrupt changes in readings. Additionally, other substances in the environment can also interfere with detection. For example, high concentrations of dust, fumes, or other non-target flammable gases in the detection area may react with the sensor, causing signal instability. Sudden changes in temperature and humidity, such as moving from a cold outdoor environment to a hot indoor environment, can also affect sensor operation and potentially lead to unstable readings.
III. Improper Operation: Lack of Attention to Usage Details
Improper operation can also lead to fluctuating readings. For example, excessive shaking of the handheld combustible gas detector or frequent relocation during testing, before the sensor has stabilized and detected the gas concentration in the current area, will cause the readings to fluctuate with the change of detection point. If using an external sampling tube, bending, blockage, or leakage will cause unstable gas sampling, leading to fluctuating readings. Furthermore, failure to preheat the equipment according to specifications can also cause problems. Starting testing before the combustible gas detector has fully preheated will prevent the sensor from reaching a stable operating state, making the readings prone to fluctuation. Failure to perform zero-point calibration before testing will result in an inaccurate initial reference value, causing subsequent test readings to deviate from the normal range, manifesting as fluctuating readings.
IV. Troubleshooting and Solutions
First, check the condition of the combustible gas detector. Look for obvious stains or damage to the sensor; clean or replace it if necessary. Check the battery power and whether the interface is oxidized; replace the battery or clean the interface if necessary. For equipment with a sampling pump, test whether the gas extraction is uniform; repair or replace the pump if the speed is abnormal.
Next, optimize the testing environment and operation. Avoid areas with strong airflow and test in a stable environment. Keep the combustible gas detector stable during testing; avoid frequent movement. Hold the detector at the same point for a while until the value stabilizes before recording. If using a sampling tube, ensure the tube is unobstructed, without bends or leaks.
Finally, calibrate and preheat according to specifications. Before each use of the combustible gas detector, perform zero-point calibration according to the instruction manual. After powering on, wait for preheating to complete and the value to stabilize before testing. If the values still fluctuate after troubleshooting, it may be an internal hardware failure; it is recommended to contact the manufacturer for professional testing and repair.